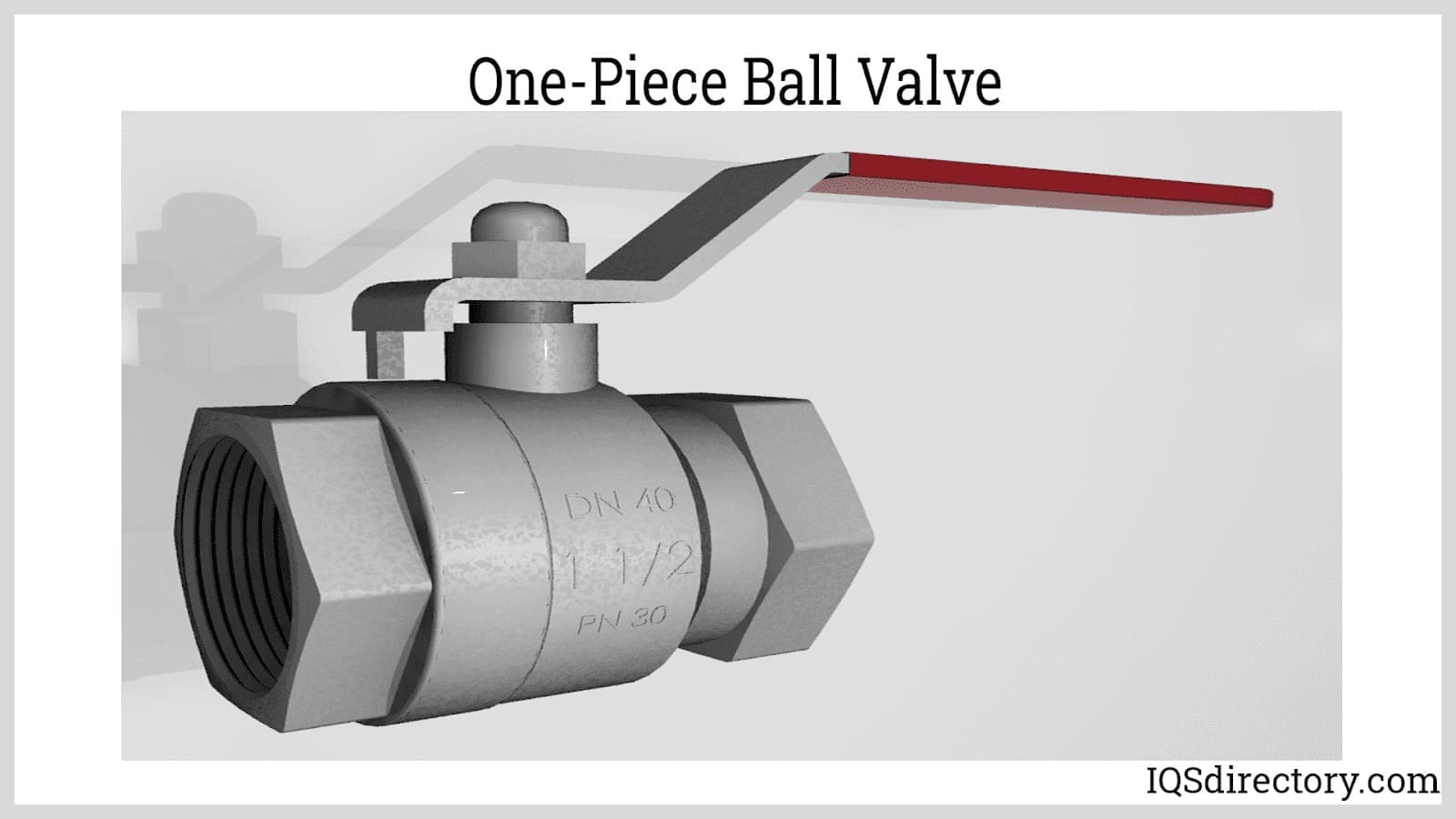
Ball valves are commonly used in various industrial settings to regulate the flow of fluids or gasses. High-pressure ball valves, as the name suggests, are designed to withstand higher pressures than standard ball valves.High-pressure ball valves are essential components in industries that require the regulation of fluids or gasses under high pressure. They are engineered to withstand high pressure and provide reliable and precise control of fluid flow. Read More…
United States Plastic Corp. manufactures and distributes some 25,000 plastic items serving over 85,000 clients operating in a factory five acres under roof. Our major product is manufacturing plastic tanks, the distribution of bottles, carboy and plastic containers. This also includes plastic sheet, rods, tubes, flexible tubing and thousands of plastic fittings.
Valworx offers ball valves in Stainless Steel, Sanitary, Brass and PVC. Our standard quarter-turn ball valves use handles for manual operation. For actuation, some ball valves feature a mounting pad cast into the housing for mounting directly to pneumatic or electric actuators. Actuated ball valve assemblies are typically used for On/Off or modulating control of water, air, oil and other...

C & C Industries offers high-quality threaded brass ball valves through 4" rated to 600# WOG and carbon steel and ductile iron ball valves through 3" rated up to 5000# WOG. In addition, C & C Industries offers a full line of flanged products in both floating and trunnion design.

Offering a full line of flow control products, Plast-O-Matic Valves ensures high quality by testing each of our valve products individually before shipment. We offer plastic check valves, PVC check valves, relief valves, ball check valves and more. We are committed to engineering excellence.

More High Pressure Ball Valve Manufacturers
How High-Pressure Ball Valves Work
High-pressure ball valves, a critical component in industrial flow control, are specifically engineered to operate reliably at elevated pressure ranges that exceed the capabilities of standard ball valves. Their primary function is to regulate, isolate, or shut off the flow of fluids or gases within a pipeline system. The internal mechanism utilizes a solid, machined ball with a central bore. When the valve handle rotates the ball, the bore aligns with the pipeline to permit flow or turns perpendicular to block passage, ensuring a tight shutoff. This robust design, often reinforced with high-integrity seats and seals, enables high-pressure ball valves to maintain leak-free operation even in extreme pressure environments, making them indispensable for high-demand applications.
Looking to understand what sets high-pressure ball valves apart from standard valves? High-pressure ball valves are distinguished by their pressure ratings, typically ranging from 3,000 PSI up to 10,000 PSI and beyond, depending on the construction and material selection. These valves are engineered for critical process applications where reliability and safety are paramount, such as in oil and gas transmission, hydraulic systems, and power generation. Their capability to deliver bubble-tight shutoff and rapid operation under high stress makes them a popular choice for industries seeking robust, low-maintenance solutions for demanding environments.
- Key features include high-cycle durability, full-port or reduced-port configurations, anti-blowout stems, and advanced packing systems to prevent leakage.
- Common actuation methods: manual lever, pneumatic actuator, electric actuator, and hydraulic operation for remote or automated control.
- Available in both two-way and three-way configurations for versatile flow path management.
Materials Used in High-Pressure Ball Valves
The choice of material in high-pressure ball valve construction is vital to ensure safety, durability, and chemical compatibility. Manufacturers select materials based on the intended application, fluid media, operating temperature, and pressure requirements. The most common materials include:
- Brass: Ideal for low to moderate pressure water, air, and non-corrosive fluid applications. Brass offers good machinability and corrosion resistance but is limited by its lower strength at high pressures.
- Stainless Steel: The preferred material for high-pressure environments, especially grades 316 and 304 stainless steel, which provide exceptional corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and compatibility with aggressive chemicals, seawater, and extreme temperatures.
- Carbon Steel: Favored for its robustness and cost-effectiveness in high-pressure, high-temperature applications where corrosion is not a primary concern. Carbon steel high-pressure ball valves are commonly used in oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation industries.
- Super Alloys (e.g., Monel, Hastelloy, Inconel): Utilized for highly corrosive or extreme temperature applications that exceed the limits of stainless or carbon steel.
- Plastic and Composite Materials: Used in select chemical processing environments where aggressive media require non-metallic wetted surfaces. However, these are typically limited to lower pressure ratings.
Seats, seals, and packing are typically made from advanced polymers such as PTFE (Teflon), PEEK, or reinforced elastomers, chosen for their chemical compatibility and resilience to pressure cycling. Ensuring the right material selection is crucial for maximizing lifespan and minimizing the risk of valve failure or leakage in high-pressure systems.
Wondering which material is best for your specific high-pressure application? Contact an expert to discuss your process requirements, media compatibility, and environmental factors to ensure optimal valve performance and longevity.
Considerations When Selecting High-Pressure Ball Valves
Choosing the right high-pressure ball valve involves evaluating several technical and operational factors. The reliability and safety of your flow control system depend on matching valve specifications to application demands. Consider the following key elements during the selection process:
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Confirm that the valve's maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) and temperature thresholds exceed or match your system's requirements. Over-specifying can lead to unnecessary costs, while under-specifying can cause catastrophic failures.
- Media Compatibility: Ensure that all valve wetted parts are compatible with the fluids or gases being conveyed to prevent chemical attack, corrosion, or material degradation.
- Valve Size and Flow Coefficient (Cv): Proper sizing is critical for maintaining desired flow rates and minimizing pressure drop. Consult manufacturer flow charts to select the right bore diameter for your system.
- Connection Types: High-pressure ball valves are available with threaded (NPT, BSP), flanged, welded, or compression end connections. Select the connection style that matches your piping system and pressure requirements.
- Actuation Method: Determine if manual, pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuation is required based on accessibility, automation needs, and safety protocols.
- Certifications and Standards: Look for compliance with industry standards such as API 6D, ASME B16.34, ISO 5211, and relevant fire-safe and fugitive emissions certifications.
Are you unsure how to size a high-pressure ball valve or which connection type is best? Ask our technical team for personalized recommendations.
Common Challenges and Maintenance Considerations
Manufacturing and maintaining high-pressure ball valves involve overcoming several engineering challenges. The most critical concern is ensuring leak-tight performance under extreme pressures, especially during frequent actuations or in environments with rapid pressure cycling. Here are some important points to consider:
- Sealing Systems: Advanced seat and packing designs — including live-loaded or spring-energized seals — are crucial to prevent leakage and maintain integrity over time.
- Thermal Expansion and Pressure Spikes: Valves must be designed to accommodate changes in temperature and sudden pressure surges, which can otherwise lead to seat extrusion or stem damage.
- Wear and Tear: High-cycle applications demand materials with high wear resistance and the ability to withstand abrasion and erosion from process media.
- Routine Maintenance: Regular inspection, lubrication, and timely replacement of seals or seats are essential for preventing leaks and ensuring long service life. Some high-pressure ball valves are designed for easy in-line maintenance and repair.
Benefits of High-Pressure Ball Valves
High-pressure ball valves deliver a multitude of benefits that make them the go-to solution for critical flow control in demanding environments. Whether you are managing hazardous chemicals, controlling steam in a power plant, or regulating high-pressure hydraulic fluids, these valves offer distinct advantages:
Durability and Longevity
Engineered for extreme service, high-pressure ball valves are constructed from premium-grade materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and corrosion-resistant alloys. This robust construction ensures excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and fatigue, resulting in significantly reduced maintenance costs and extended service intervals. Many models are designed to exceed industry cycle life requirements, providing years of reliable operation in challenging conditions.
Precise and Reliable Flow Control
With precise quarter-turn operation, high-pressure ball valves offer accurate modulation of flow rates. This makes them ideal for processes requiring tight control over fluid or gas movement — such as chemical dosing, water treatment, and gas distribution systems. The low-torque operation also facilitates easy actuation, whether manual or automated.
Leak Prevention and Safety
Advanced seat and packing designs ensure bubble-tight shutoff, minimizing the risk of leaks that could endanger personnel, damage equipment, or cause environmental contamination. Safety features, such as locking handles and anti-static devices, further enhance operational security, making these valves suitable for use in hazardous or regulated environments.
Versatility Across Applications
High-pressure ball valves excel in a wide range of applications, including high-pressure steam, gas, oil, water, hydraulic systems, and aggressive chemicals. Available in various configurations — such as two-way, three-way, trunnion-mounted, and floating ball designs — they support diverse process needs across multiple industries.
Cost-Effectiveness
Thanks to their long service life, minimal maintenance requirements, and reliable performance, high-pressure ball valves offer a competitive total cost of ownership (TCO). Their straightforward design allows for easy installation and integration with existing systems, further reducing project costs.
Ease of Operation and Automation
Designed for operator convenience, most high-pressure ball valves require minimal force for actuation. They are also compatible with a variety of actuators, including pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic, enabling integration into fully automated process control systems for improved efficiency and safety.
Compliance and Industry Standards
Many high-pressure ball valves are manufactured to meet or exceed industry standards including API, ASME, ISO, and NACE, ensuring consistent quality, reliability, and regulatory compliance for critical applications.
Applications of High-Pressure Ball Valves
Thanks to their robust design and versatile performance characteristics, high-pressure ball valves are used across a variety of industries and systems where reliable flow control at elevated pressures is essential. Typical application areas include:
Oil and Gas Industry
Essential in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, high-pressure ball valves control the flow of crude oil, refined products, and natural gas. They are used in wellheads, separation systems, pipeline transmission lines, and offshore drilling platforms, where safety and reliability are non-negotiable.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
High-pressure ball valves are integral to chemical plants, refineries, and petrochemical facilities. They manage the flow of aggressive chemicals, acids, solvents, and high-temperature fluids, providing precise control and leak-tight shutoff to protect process integrity and safety.
Water Treatment and Distribution
In municipal and industrial water treatment facilities, high-pressure ball valves regulate the flow of water, steam, and treatment chemicals. Their corrosion resistance and tight shutoff help maintain water quality and system reliability.
Aerospace and Defense
Critical for high-pressure hydraulic, fuel, and coolant circuits in aerospace and defense systems, these valves are designed to meet stringent performance and safety standards required in mission-critical applications such as rocket engines, ground support equipment, and military vehicles.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
Used for sterile and high-purity process control, high-pressure ball valves in this sector are manufactured from sanitary-grade stainless steel and feature easy-clean designs. They support precise dosing and transfer of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), solvents, and process gases.
Food and Beverage Processing
High-pressure ball valves play a vital role in maintaining hygienic fluid handling in food and beverage production. They are used for the safe transfer of high-pressure water, syrups, and CIP (clean-in-place) solutions in compliance with food safety standards.
Power Generation and Utilities
Steam, superheated water, and high-pressure process fluids are safely managed using high-pressure ball valves in thermal and nuclear power plants. Their reliability and resilience under cyclic loading are crucial for boiler, turbine, and auxiliary fluid systems.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
In industrial automation and heavy machinery, high-pressure ball valves control hydraulic fluids and compressed air, providing precise, safe, and maintenance-friendly operation for actuators, presses, and power units.
Buying Guide: Choosing the Right High-Pressure Ball Valve Supplier
Identifying the ideal high-pressure ball valve supplier is a decisive step in ensuring system performance, safety, and long-term value. Here’s a structured approach to making the right supplier choice:
- Evaluate supplier expertise in your specific industry (e.g., oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment).
- Check for certifications and quality assurance programs (API, ISO, ASME) that demonstrate product reliability and regulatory compliance.
- Assess the supplier’s customization capabilities for unique material, size, or actuation requirements.
- Review warranty terms, lead times, after-sales support, and availability of technical documentation.
- Compare pricing structures and total cost of ownership (TCO), not just upfront costs.
- Read case studies, testimonials, and references to verify performance in similar applications.
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing high-pressure ball valves from a high-pressure ball valve supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of high-pressure ball valve suppliers. Each high-pressure ball valve supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or to request a quote. Review each high-pressure ball valve business website using our proprietary website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple high-pressure ball valve companies with the same form.
Frequently Asked Questions About High-Pressure Ball Valves
- What pressure ratings are available for high-pressure ball valves?
Most manufacturers offer high-pressure ball valves rated from 3,000 PSI to as high as 15,000 PSI or more, depending on size, material, and design specification. - Can high-pressure ball valves be automated?
Yes, they can be fitted with pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuators for remote or automated control, supporting integration into industrial control and safety systems. - What maintenance is required for reliable operation?
Routine inspection, periodic lubrication, and timely replacement of seats and seals are recommended. Some designs allow for in-line maintenance to reduce downtime. - Are high-pressure ball valves suitable for corrosive or hazardous fluids?
When constructed from appropriate materials (such as 316 stainless, Monel, or Hastelloy) and equipped with compatible seals, they are ideal for aggressive or hazardous media. - How do I select the correct size and configuration?
Consult manufacturer sizing charts and application engineers to ensure the valve matches your flow, pressure, and connection requirements.
Next Steps: Sourcing and Specification Assistance
Are you ready to specify or purchase high-pressure ball valves for your next project? Our supplier directory and technical resources can help you:
- Compare leading high-pressure ball valve manufacturers side-by-side
- Download product datasheets, CAD drawings, and material certifications
- Request custom-engineered solutions for unique process requirements
- Access technical support to resolve selection or maintenance questions
- Submit a Request for Quote (RFQ) to multiple suppliers with a single form
For more information about selecting, specifying, or maintaining high-pressure ball valves, contact our technical team or browse our supplier directory to find a trusted partner who can support your application from design through operation.
Contact an Expert
Have specific questions about high-pressure ball valves, technical challenges, or supplier selection? Contact our technical team to get answers, request application engineering support, or discuss custom solutions tailored to your operational needs.
Maintenance Best Practices Guide
To maximize the performance and lifespan of your high-pressure ball valves, follow our comprehensive maintenance best practices guide for step-by-step instructions on inspection, lubrication, troubleshooting, and replacement of critical components.







 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services