When the pressure reaches a certain level, the ball drifts downstream and tightly pushes against the seat. The seat must be made of strong materials because it bears the force of the pressure when the ball comes into contact with it. Floating ball valves are constructed from stainless steel, brass or other metals. Read More…
United States Plastic Corp. manufactures and distributes some 25,000 plastic items serving over 85,000 clients operating in a factory five acres under roof. Our major product is manufacturing plastic tanks, the distribution of bottles, carboy and plastic containers. This also includes plastic sheet, rods, tubes, flexible tubing and thousands of plastic fittings.
Valworx offers ball valves in Stainless Steel, Sanitary, Brass and PVC. Our standard quarter-turn ball valves use handles for manual operation. For actuation, some ball valves feature a mounting pad cast into the housing for mounting directly to pneumatic or electric actuators. Actuated ball valve assemblies are typically used for On/Off or modulating control of water, air, oil and other...

C & C Industries offers high-quality threaded brass ball valves through 4" rated to 600# WOG and carbon steel and ductile iron ball valves through 3" rated up to 5000# WOG. In addition, C & C Industries offers a full line of flanged products in both floating and trunnion design.

Offering a full line of flow control products, Plast-O-Matic Valves ensures high quality by testing each of our valve products individually before shipment. We offer plastic check valves, PVC check valves, relief valves, ball check valves and more. We are committed to engineering excellence.

More Floating Ball Valve Manufacturers
Floating Ball Valves: Design, Applications, and Industry Insights
Floating ball valves are a fundamental component in modern fluid control systems, prized for their reliable shut-off capabilities and versatility across numerous industries. These valves feature a unique design where the ball inside may have a ceramic center, typically coated in chrome or other corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability and longevity. Floating ball valves are commonly utilized in low or moderate pressure applications, offering robust performance in managing the flow of liquids and gases. Their widespread use spans the chemical processing industry, pharmaceutical manufacturing, oil and gas production, water treatment facilities, and various other sectors that rely on precise flow regulation within pipeline systems.
What Is a Floating Ball Valve? Understanding the Core Design
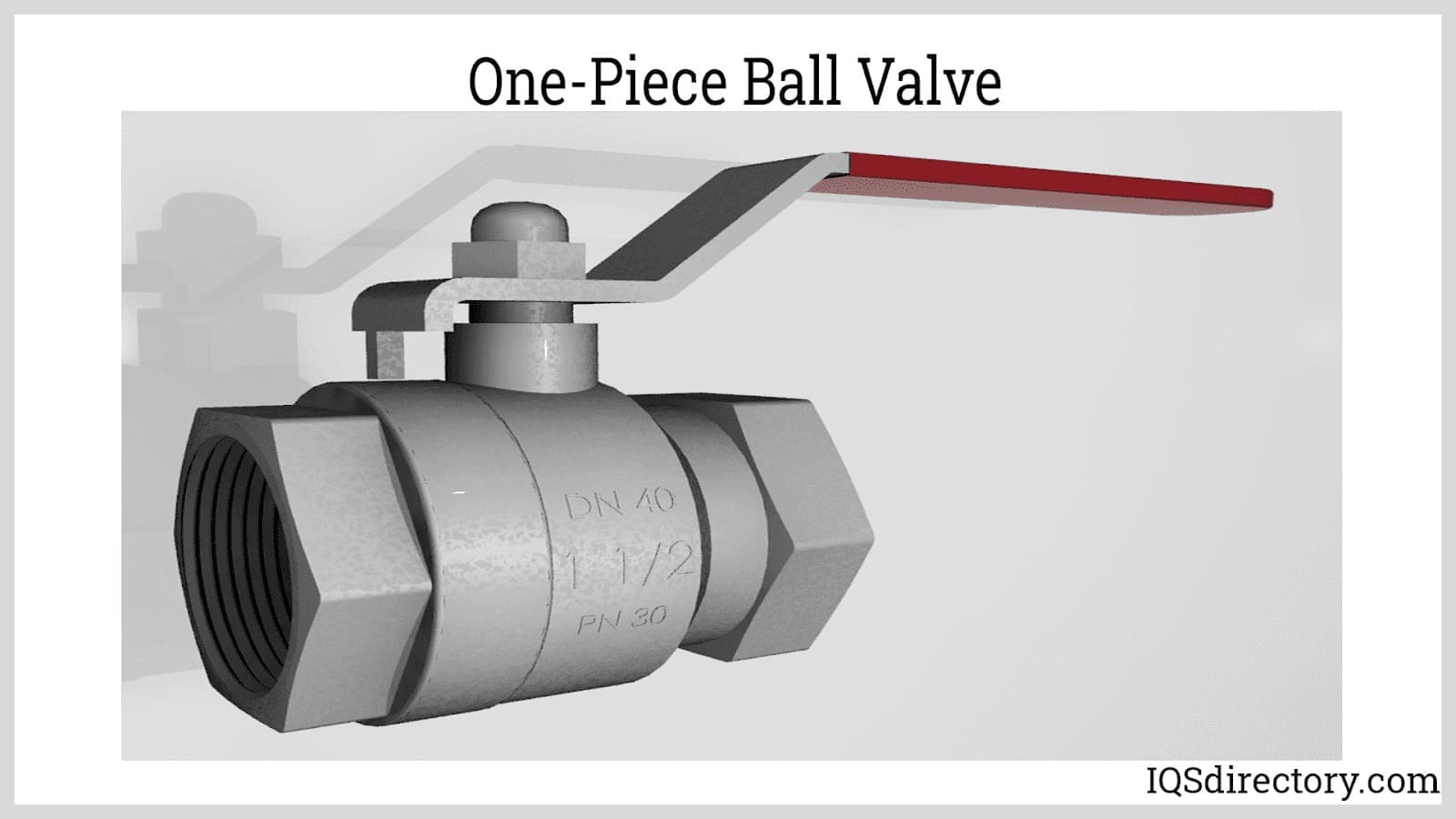
At their core, floating ball valves are nearly identical to conventional ball valves in both structure and function, with one crucial distinction. In both designs, a spherical ball—featuring a straight-through bore or hole—serves as the flow control mechanism. When the valve is open, fluids flow freely through this central opening. To stop the flow, the ball is rotated 90 degrees, positioning the hole perpendicular to the direction of the pipe and thereby creating a tight seal that blocks passage completely.
The actuation of the floating ball is achieved via a stem or shaft, which connects the ball to an actuator. This actuator may take the form of a manual lever, a handwheel, or an electrically-powered motor, depending on system requirements and automation levels. In floating ball valves, the ball is designed to "float" slightly downstream, coming into contact with the downstream seat where the primary sealing occurs. This feature distinguishes floating ball valves from trunnion-mounted ball valves, which use additional support mechanisms to hold the ball in place.
How Does a Floating Ball Valve Work?
Floating ball valves excel in providing reliable shut-off and flow control in pipelines. The unique "floating" mechanism allows the ball to move slightly along the axis of the pipe under pressure. When system pressure is low, the floating ball makes light contact with the downstream sealing ring, allowing the liquid or gas to flow almost uninhibited.
As internal pressure increases, the force exerted by the fluid pushes the ball more firmly against the seat, creating a stronger and more reliable seal. This self-energizing sealing action is especially valuable in applications where leak-tight performance is critical. Once the actuator is engaged, the ball rotates quickly, moving the bore out of alignment with the pipe and blocking off the flow path. Despite the valve’s name, the actual movement of the ball is minimal—limited to a small axial shift within the valve body.
Key Components of Floating Ball Valves
- Ball: Often made from stainless steel, chrome-plated brass, or ceramic materials for enhanced corrosion resistance and durability.
- Seats: Typically constructed from PTFE (Teflon), reinforced polymers, or metallic alloys to ensure a tight seal and minimize leakage.
- Stem/Shaft: Connects the ball to the actuator; designed to withstand both torque and pressure variations.
- Body: Available in one-piece, two-piece, or three-piece designs for varying degrees of serviceability and installation flexibility.
- Actuator: Can be manually operated or automated for remote control and integration with process systems.
Where Are Floating Ball Valves Used? Industry Applications and Use Cases
Floating ball valves are highly valued for their versatility and reliability across a broad range of industries. Common applications include:
- Chemical Manufacturing: For handling corrosive and hazardous chemicals that require safe, leak-proof shut-off.
- Pharmaceutical Processing: Ensuring sanitary flow conditions and preventing contamination in cleanroom environments.
- Oil and Gas: Used in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations to control the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products.
- Water Treatment and Distribution: Regulating potable water, wastewater, and industrial process water in municipal and industrial facilities.
- HVAC & Building Services: Managing heating and cooling fluids in commercial and residential buildings.
- Food and Beverage: Maintaining hygienic conditions in processing lines for beverages, dairy, and other consumables.
- Pulp and Paper: Handling slurries and liquid-solid mixtures that demand robust sealing and abrasion resistance.
Are you looking for the best floating ball valve for your application? Compare floating ball valve specifications, material options, and certifications to ensure compatibility with your process requirements. For assistance, consider reviewing our Ball Valve Buyers Guide for in-depth selection tips and best practices.
What Are the Advantages of Floating Ball Valves?
Floating ball valves are engineered for performance, safety, and ease of use. Their key benefits include:
- Reliable Shut-Off: The floating design creates a bubble-tight seal, making these valves ideal for applications where zero leakage is critical.
- Simple Operation: A quarter-turn action simplifies manual or automated control, reducing operator fatigue and system complexity.
- Compact Footprint: Floating ball valves are typically more compact than trunnion-mounted designs, making them suitable for space-constrained installations.
- Versatile Materials: Available in a wide range of body and seat materials, including stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and various polymers, to accommodate diverse media and operating conditions.
- Low Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and a straightforward mechanism, floating ball valves are easy to maintain and service.
- Cost-Effective: Their simple design often results in lower manufacturing and maintenance costs compared to more complex valve types.
Wondering how to maximize the lifespan of your floating ball valves? Regular maintenance, correct installation, and selecting the right materials based on your process conditions are essential. Learn more in our Ball Valve Maintenance Guide.
Floating Ball Valves vs. Trunnion Ball Valves: Which Is Right for Your System?
When choosing between floating ball valves and trunnion-mounted ball valves, it's important to understand the key differences and application considerations:
- Floating Ball Valves: Best suited for low to moderate pressure systems (typically up to 600 psi) and smaller pipe sizes. Their simple, compact design makes them ideal for general service and isolation duties.
- Trunnion Ball Valves: Designed for high-pressure, large-diameter pipelines. The ball is supported by trunnions, reducing seat wear and lowering operating torque. Common in oil and gas transmission, petrochemical, and power generation.
Still unsure which ball valve type is best for your project? Ask yourself:
- What are the pressure and temperature requirements of my application?
- What type of media (liquid, gas, slurry) will the valve control?
- Is tight shut-off or ease of maintenance more important for my process?
- What certifications, such as API, ISO, or FDA, are required for compliance?
Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Floating Ball Valve
Choosing the right floating ball valve involves careful consideration of several technical and operational factors:
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the valve body and seat materials are compatible with your process media to prevent corrosion, abrasion, or contamination.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Confirm the valve is rated for your maximum operating conditions. Ratings can vary significantly based on materials and design.
- End Connections: Options include threaded, flanged, welded, and socket ends to suit your piping configuration.
- Actuation Method: Decide between manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuation based on system automation needs.
- Certifications and Standards: Look for compliance with industry standards such as API 6D, ISO 5211, ASME, and others relevant to your application.
- Fire-Safe and Anti-Static Design: For hazardous environments, select valves with fire-safe and anti-static features to enhance safety.
Ready to request a quote or compare suppliers? Contact leading floating ball valve manufacturers or use our online quote request tool for fast, competitive pricing from trusted vendors.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices for Floating Ball Valves
Proper installation and regular maintenance are critical for ensuring the safe, long-term operation of floating ball valves. Follow these guidelines:
- Installation: Verify that the valve is oriented correctly and aligned with the pipeline. Use appropriate gaskets and torque settings for leak-free connections.
- Commissioning: Perform a pressure test after installation to confirm sealing integrity and functionality.
- Routine Inspection: Periodically inspect for signs of seat wear, corrosion, or leakage. Replace components as needed.
- Lubrication: Apply suitable lubricants to the stem and seats to minimize friction and extend service life.
- Actuator Testing: Test manual and automated actuators regularly to ensure reliable operation in emergency situations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Floating Ball Valves
- Q: What is the difference between a floating and a trunnion ball valve?
A: A floating ball valve has a ball that is free to move slightly along the axis of flow, using pressure to seal against the downstream seat, making it suitable for low to moderate pressures. A trunnion ball valve features additional support for the ball, allowing for use in high-pressure, large diameter pipelines. - Q: Can floating ball valves be used for throttling?
A: Floating ball valves are generally not recommended for throttling applications, as partial opening may cause seat damage and reduce sealing performance. They are best used for on-off, isolation, or shut-off purposes. - Q: What materials are available for floating ball valves?
A: Typical materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, bronze, and specialty alloys. Seats are often made from PTFE, reinforced polymers, or metallic materials for enhanced chemical compatibility and durability. - Q: Are floating ball valves suitable for high-temperature service?
A: Many floating ball valves are designed for moderate temperatures; however, high-temperature versions are available with metal seats and specialized gaskets. Always check manufacturer specifications for temperature ratings.
Future Trends and Innovations in Floating Ball Valve Technology
The floating ball valve market continues to evolve with advancements in materials science, automation integration, and smart monitoring systems. Modern designs now feature:
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Use of advanced alloys and coatings to improve performance in aggressive chemical environments.
- Smart Valves: Integration with IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of valve position, pressure, and leakage, enabling predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
- Fire-Safe and Anti-Static Designs: Improved safety features for hazardous process industries.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Adoption of sustainable materials and greener production processes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Floating Ball Valve for Your Needs
Floating ball valves remain a pivotal solution for reliable, efficient, and cost-effective fluid control across multiple sectors. Whether you operate a chemical plant, water treatment facility, or oil and gas installation, selecting the appropriate valve type, materials, and features is essential to optimizing safety and performance. By understanding the specific requirements of your application, evaluating industry certifications, and leveraging the latest innovations, you can ensure the longevity and reliability of your pipeline systems.
Ready to take the next step? Explore our curated directory of top floating ball valve manufacturers, download technical datasheets, or request a custom quote to find the best solution for your project. For further guidance, check out our Ball Valve Buyers Guide or contact our team of valve experts today.







 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
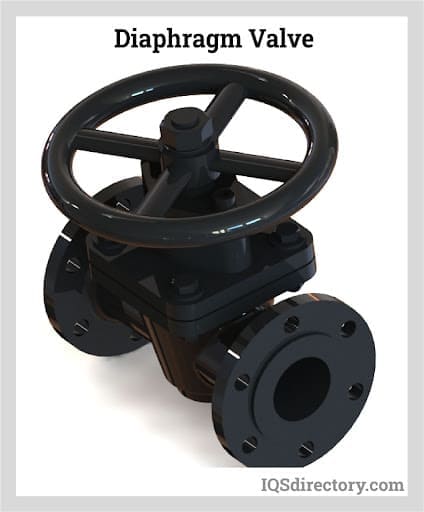
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services